Bulk Material Testing for Technical Silo Design
Silo design bulk material testing ✓ Flowability determination ✓ Wall friction analysis ✓ Engineering calculations ✓ Safe silo construction
Technical silo design requires accurate knowledge of the mechanical properties of the stored bulk material. Standards recommend measured characteristic values over estimates or table lookups.
Relevant bulk material parameters
To predict bulk material behaviour and to calculate structural loads on the silo, at least the following parameters are required:
From flowability (flow function) tests:
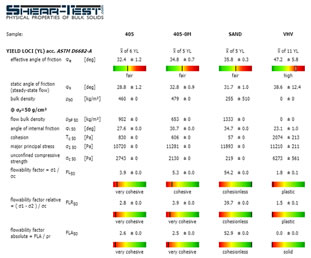
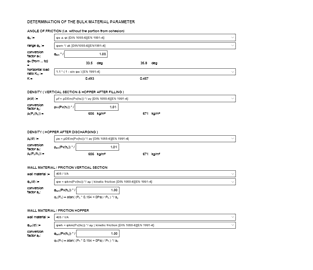
effective internal friction angle
horizontal stress ratio (λ)
cohesion / unconfined compressive strength
From wall friction tests:
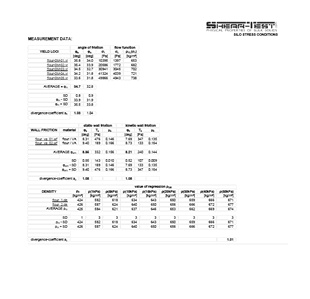
wall friction coefficient or wall friction angle
From density tests:
bulk density
compression density
Supplementary parameters:
- angle of repose
- time consolidation / ageing (flowability)
- time-dependent wall friction changes
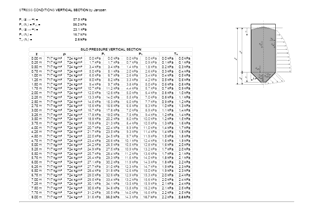
Stresses in the silo
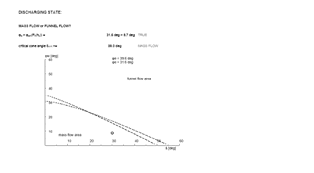
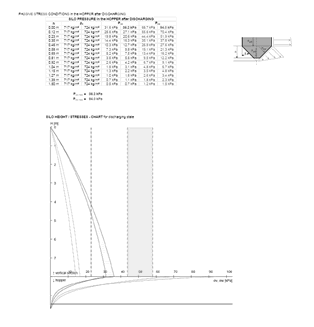
Pressure in a bulk-filled container is not hydrostatic. Due to internal friction, vertical stress is partially transferred into horizontal stresses. The horizontal stress ratio λ typically ranges from 0.3 to 0.6.
With depth, vertical stress increases and the bulk may consolidate. Wall friction transfers part of the vertical load to the silo shell.
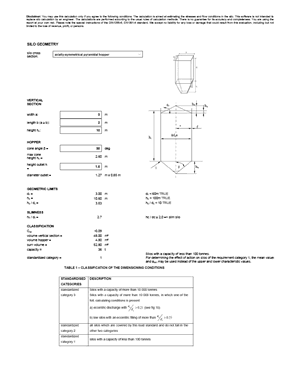
Hopper geometry
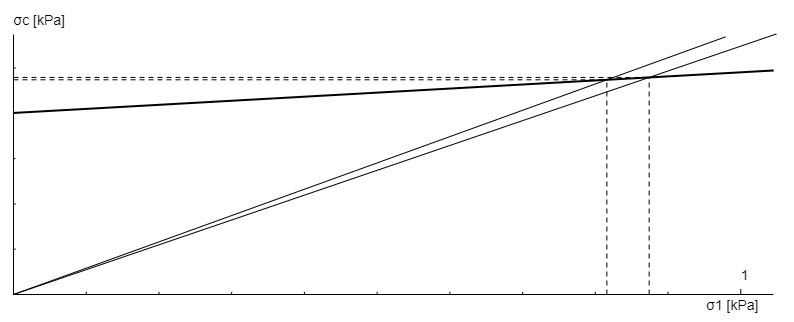
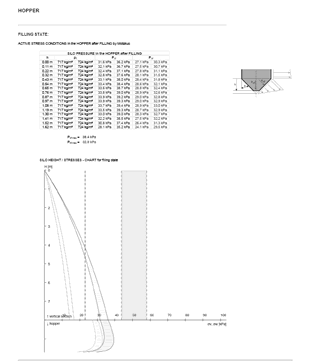
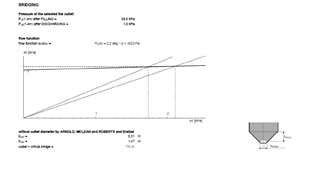
Hopper geometry strongly affects flow profiles and discharge behaviour. The flow function (σc(σ)) relates unconfined strength to the major consolidation stress and is used to compute the critical outlet diameter to avoid bridging.
|
CALCULATION OF THE CRITICAL OUTLET DIAMETER
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| flow function σc(σ) = | FL(σ) = 5.1 deg * σ + 401 Pa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| bmin = | 0.15 m | 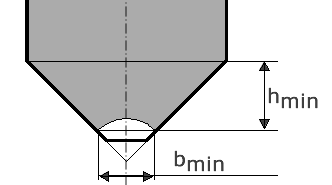 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| outlet > critical bridge = | TRUE | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Flow behaviour in the silo
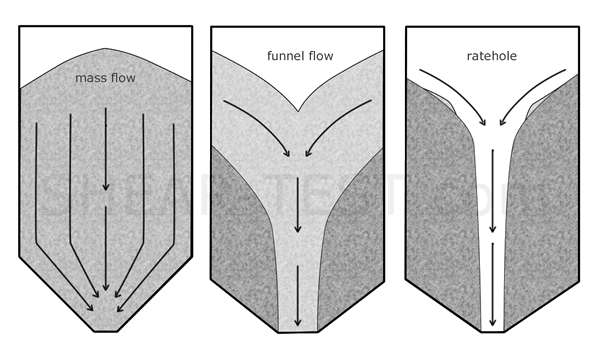
Funnel flow produces a central flow channel while surrounding material remains stagnant, causing segregation and uneven wall loads. Mass flow causes the whole inventory to move, preventing stagnation and delivering uniform discharge.
Appropriate silo design (hopper angle, outlet size, wall material) informed by measured material parameters reduces risks of bridging, ratholing and segregation.
Measurements & scope
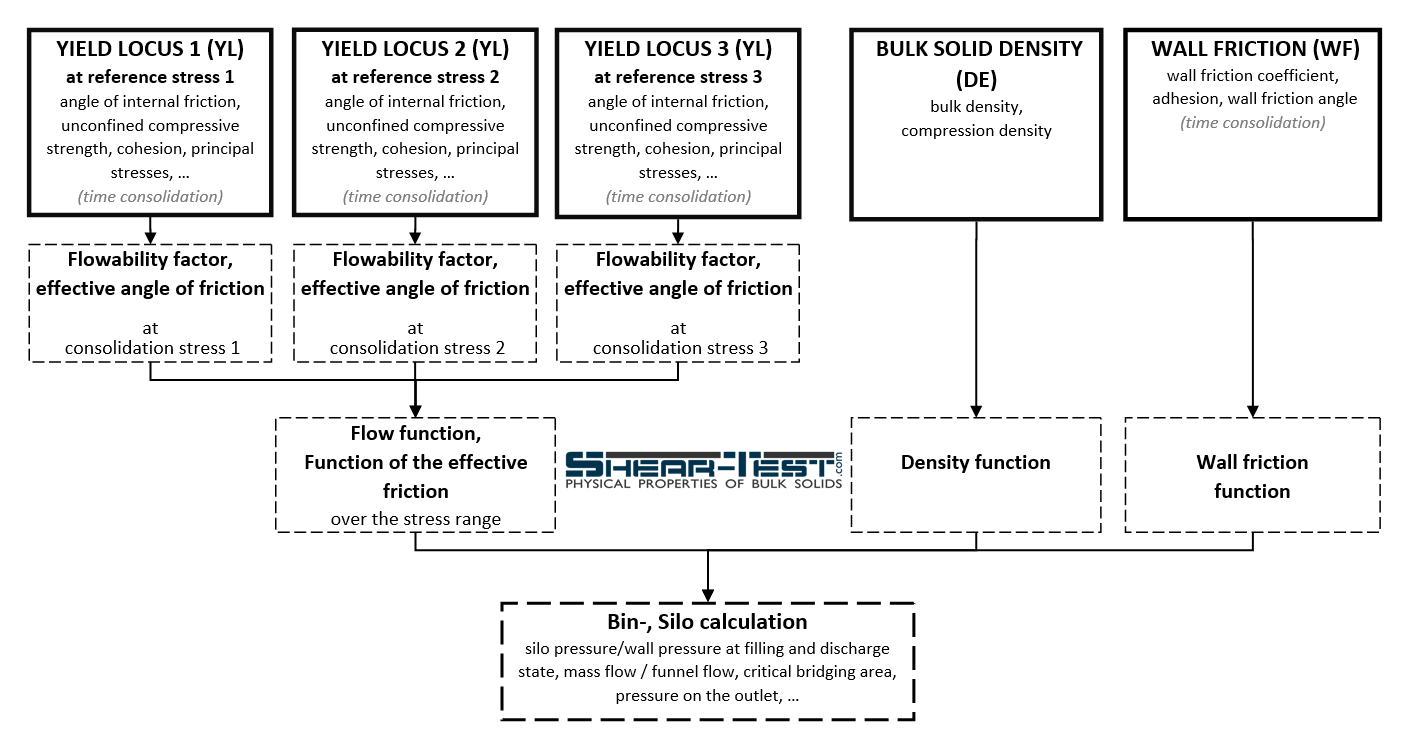
All necessary bulk material parameters for silo calculations are obtained by laboratory tests: flow function / internal friction, wall friction, bulk and compression densities. Reliance on table values or rough estimates can lead to unsafe designs.
Typical test scope for a silo calculation
- Flow function tests (YL)
at least 3 consolidation stresses σr measuring:
- effective internal friction angle
- horizontal stress ratio
- cohesion / unconfined strength - Wall friction tests (WF)
determine wall friction coefficient / angle
- Density tests (DE)
determine bulk and compression densities
- angle of repose [AR]
- time consolidation flow function [YLT]
- time-dependent wall friction [WFT]
- process-related changes of wall friction [WFC]
- moisture content determination [MO]
Contact us for consultancy and an offer for your bulk material tests.
Our laboratory provides comprehensive testing (flow function, wall friction, time consolidation) and practical silo calculations. We recommend measures to ensure mass flow.
- ✓ Tests following recognized procedures
- ✓ Online silo limit criteria
- ✓ Practical recommendations for discharge devices