Density of Bulk Materials
Bulk density fundamentals ✓ Measurement methods ✓ Silo & plant design ✓ Powders & granulates ✓ Technical relevance ✓ Practical examples
The bulk density (ρb0) is the ratio of mass (m) to the total volume (V) of a bulk material including voids and pores in the unconsolidated state. In practice a representative sample is placed into a defined container with controlled filling conditions and the mass is recorded. Bulk density is reported in [kg/m³] or [g/cm³].
Tapped Density (ρbK)
DIN EN ISO 787-11, ASTM B527Tapped density is the density after compaction by tapping, vibration or gentle impact. Depending on the standard, a sample with defined mass/volume is filled into a cylinder with minimal disturbance, the initial bulk density is determined and then the cylinder is tapped with a specified stroke and number of taps. The tapped density is the quotient of the sample mass and the resulting tapped volume.
From these data characteristic indices can be calculated:
- Hausner ratio (dimensionless): ratio of tapped volume to initial bulk volume.
- Compressibility index (%): percentage volume change on tapping for a fixed mass.
Compression Density (uniaxial) (ρbC)
ASTM-D6682-B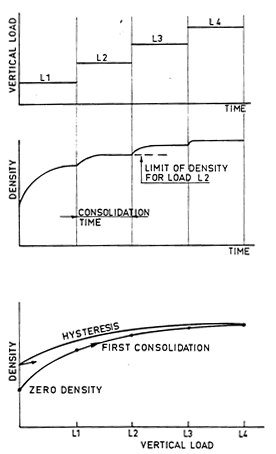
Under vertical loading (e.g. due to self-weight in storage) the packing density of a bulk material increases and voids reduce. Changes in packing density strongly affect bulk behaviour: reduced interparticle spacing increases contact area and interparticle forces.
Bulk density (ρb) is mass divided by volume. The density at zero applied pressure is the initial bulk density (ρb0). Cohesive materials often show irreversible densification and hysteresis.
Flow Density
ASTM-D6682-ADuring yield locus measurements density is recorded simultaneously under the influence of consolidation pressure and shear. While standards may focus on uniaxial compression, both uniaxial and flow (biaxial/shear) compaction can be evaluated in automated analyses.
Example: Uniaxial compression and flow density of a bulk material

Professional Density Determination for Your Bulk Material
Need precise characterisation of your bulk material? Our laboratory performs standard‑compliant bulk, tapped and compression density measurements and provides comprehensive evaluation reports.
- ✓ Over 30 years of experience
- ✓ Standard‑compliant testing procedures
- ✓ Detailed evaluation reports with recommendations
